MLflow
MLflow는 머신 러닝 실무자와 팀이 머신 러닝 프로세스의 복잡성을 처리하는 데 도움을 주기 위해 특별히 구축된 오픈 소스 플랫폼입니다. MLflow는 머신 러닝 프로젝트의 전체 수명 주기에 초점을 맞춰 각 단계가 관리 가능하고 추적 가능하며 재현 가능하도록 보장합니다. 즉, 머신러닝 학습과 관련된 전반적인 lifecycle을 지원하는 라이브러리입니다.
EDA
1
2
3
4
5
| import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import plotly.graph_objects as go
%matplotlib inline
|
데이터 셋은 다음 링크에서 받을 수 있습니다.
https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/anikannal/solar-power-generation-data
1
2
| generation = pd.read_csv("./data/Plant_1_Generation_Data.csv")
weather = pd.read_csv("./data/Plant_1_Weather_Sensor_Data.csv")
|
| DATE_TIME | PLANT_ID | SOURCE_KEY | DC_POWER | AC_POWER | DAILY_YIELD | TOTAL_YIELD |
|---|
| 0 | 15-05-2020 00:00 | 4135001 | 1BY6WEcLGh8j5v7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6259559.0 |
|---|
| 1 | 15-05-2020 00:00 | 4135001 | 1IF53ai7Xc0U56Y | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6183645.0 |
|---|
| 2 | 15-05-2020 00:00 | 4135001 | 3PZuoBAID5Wc2HD | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6987759.0 |
|---|
| 3 | 15-05-2020 00:00 | 4135001 | 7JYdWkrLSPkdwr4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 7602960.0 |
|---|
| 4 | 15-05-2020 00:00 | 4135001 | McdE0feGgRqW7Ca | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 7158964.0 |
|---|
| DATE_TIME | PLANT_ID | SOURCE_KEY | AMBIENT_TEMPERATURE | MODULE_TEMPERATURE | IRRADIATION |
|---|
| 0 | 2020-05-15 00:00:00 | 4135001 | HmiyD2TTLFNqkNe | 25.184316 | 22.857507 | 0.0 |
|---|
| 1 | 2020-05-15 00:15:00 | 4135001 | HmiyD2TTLFNqkNe | 25.084589 | 22.761668 | 0.0 |
|---|
| 2 | 2020-05-15 00:30:00 | 4135001 | HmiyD2TTLFNqkNe | 24.935753 | 22.592306 | 0.0 |
|---|
| 3 | 2020-05-15 00:45:00 | 4135001 | HmiyD2TTLFNqkNe | 24.846130 | 22.360852 | 0.0 |
|---|
| 4 | 2020-05-15 01:00:00 | 4135001 | HmiyD2TTLFNqkNe | 24.621525 | 22.165423 | 0.0 |
|---|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 68778 entries, 0 to 68777
Data columns (total 7 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 DATE_TIME 68778 non-null object
1 PLANT_ID 68778 non-null int64
2 SOURCE_KEY 68778 non-null object
3 DC_POWER 68778 non-null float64
4 AC_POWER 68778 non-null float64
5 DAILY_YIELD 68778 non-null float64
6 TOTAL_YIELD 68778 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(4), int64(1), object(2)
memory usage: 3.7+ MB
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 3182 entries, 0 to 3181
Data columns (total 6 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 DATE_TIME 3182 non-null object
1 PLANT_ID 3182 non-null int64
2 SOURCE_KEY 3182 non-null object
3 AMBIENT_TEMPERATURE 3182 non-null float64
4 MODULE_TEMPERATURE 3182 non-null float64
5 IRRADIATION 3182 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(3), int64(1), object(2)
memory usage: 149.3+ KB
|
각 DATE_TIME이 Object이기에 datetime type으로 변환시킵니다.
1
2
| generation['DATE_TIME'] = pd.to_datetime(generation['DATE_TIME'], dayfirst=True)
weather['DATE_TIME'] = pd.to_datetime(weather['DATE_TIME'], dayfirst=True)
|
1
2
| C:\Users\PC\AppData\Local\Temp\ipykernel_24200\2802134372.py:2: UserWarning: Parsing dates in %Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S format when dayfirst=True was specified. Pass `dayfirst=False` or specify a format to silence this warning.
weather['DATE_TIME'] = pd.to_datetime(weather['DATE_TIME'], dayfirst=True)
|
1
2
| generation_source_key = list(generation['SOURCE_KEY'].unique())
print('generation source key 갯수 :', len(generation_source_key))
|
1
| generation source key 갯수 : 22
|
generation의 설비는 총 22개이므로 이 중 1개의 설비만을 분석하고자 합니다.
1
2
3
| inv = generation[generation['SOURCE_KEY']==generation_source_key[0]]
mask = ((weather['DATE_TIME'] >= min(inv["DATE_TIME"])) & (weather['DATE_TIME'] <= max(inv["DATE_TIME"])))
weather_filtered = weather.loc[mask]
|
1
2
3
| df = inv.merge(weather_filtered, on="DATE_TIME", how='left')
df = df[['DATE_TIME', 'AC_POWER', 'AMBIENT_TEMPERATURE', 'MODULE_TEMPERATURE', 'IRRADIATION']]
df.head()
|
| DATE_TIME | AC_POWER | AMBIENT_TEMPERATURE | MODULE_TEMPERATURE | IRRADIATION |
|---|
| 0 | 2020-05-15 00:00:00 | 0.0 | 25.184316 | 22.857507 | 0.0 |
|---|
| 1 | 2020-05-15 00:15:00 | 0.0 | 25.084589 | 22.761668 | 0.0 |
|---|
| 2 | 2020-05-15 00:30:00 | 0.0 | 24.935753 | 22.592306 | 0.0 |
|---|
| 3 | 2020-05-15 00:45:00 | 0.0 | 24.846130 | 22.360852 | 0.0 |
|---|
| 4 | 2020-05-15 01:00:00 | 0.0 | 24.621525 | 22.165423 | 0.0 |
|---|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 3154 entries, 0 to 3153
Data columns (total 5 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 DATE_TIME 3154 non-null datetime64[ns]
1 AC_POWER 3154 non-null float64
2 AMBIENT_TEMPERATURE 3154 non-null float64
3 MODULE_TEMPERATURE 3154 non-null float64
4 IRRADIATION 3154 non-null float64
dtypes: datetime64[ns](1), float64(4)
memory usage: 123.3 KB
|
1
2
| df_timestamp = df[["DATE_TIME"]]
df_ = df[["AC_POWER", "AMBIENT_TEMPERATURE", "MODULE_TEMPERATURE", "IRRADIATION"]]
|
모델을 train과 validation으로 분리합니다.
1
2
3
| train_prp = .6
train = df_.loc[:df_.shape[0]*train_prp]
test = df_.loc[df_.shape[0]*train_prp:]
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
X_train = scaler.fit_transform(train)
X_test = scaler.transform(test)
X_train = X_train.reshape(X_train.shape[0], 1, X_train.shape[1])
X_test = X_test.reshape(X_test.shape[0], 1, X_test.shape[1])
print(f"X_train shape: {X_train.shape}")
print(f"X_test shape: {X_test.shape}")
|
1
2
| X_train shape: (1893, 1, 4)
X_test shape: (1261, 1, 4)
|
Model design
1
2
3
| import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, TensorDataset
|
LSTMAutoencoder라는 모델을 사용해서 시계열 이상탐지를 진행하고자 합니다. 위 자세한 사항은 Unsupervised Learning of Video Representations using LSTMs을 참고하시면 됩니다.
추후에 LSTMAutoencoder를 정리해보겠습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| class LSTMAutoencoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, seq_len, n_features):
super(LSTMAutoencoder, self).__init__()
# 인코더
self.encoder_lstm1 = nn.LSTM(input_size=n_features, hidden_size=16, batch_first=True)
self.encoder_lstm2 = nn.LSTM(input_size=16, hidden_size=4, batch_first=True)
# 디코더
self.decoder_lstm1 = nn.LSTM(input_size=4, hidden_size=4, batch_first=True)
self.decoder_lstm2 = nn.LSTM(input_size=4, hidden_size=16, batch_first=True)
self.decoder_output = nn.Linear(16, n_features)
self.seq_len = seq_len
def forward(self, x):
x, _ = self.encoder_lstm1(x)
x, (h_n, _) = self.encoder_lstm2(x)
x = h_n.repeat(self.seq_len, 1, 1).permute(1, 0, 2)
x, _ = self.decoder_lstm1(x)
x, _ = self.decoder_lstm2(x)
x = self.decoder_output(x)
return x
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| def model_traning(epochs, learning_rate, dataloader):
model = LSTMAutoencoder(seq_len=X_train.shape[1], n_features=X_train.shape[2])
criterion = nn.L1Loss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
epoch_loss = 0
for batch_x, _ in dataloader:
output = model(batch_x)
loss = criterion(output, batch_x)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
epoch_loss += loss.item()
if (epoch+1) % 10 == 0:
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{epochs}, Loss: {epoch_loss:.4f}")
return model
|
Model Optimization
mlflow를 사용하기 위해서는 mlflow ui를 실행했을 때, 사용되는 URI를 입력합니다.
실행하기 이전에 위 명령어를 실행시켜야 합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
| import mlflow
from mlflow.data.pandas_dataset import PandasDataset
mlflow.set_tracking_uri("http://127.0.0.1:5000")
# mlflow.create_experiment("mlflow-lab")
|
mlflow ui에서 Experiments라고 실험을 분리할 수 있습니다. 저는 mlflow-lab에 분리하여 진행하겠습니다.
1
| mlflow.set_experiment("mlflow-lab")
|
1
| <Experiment: artifact_location='mlflow-artifacts:/148508904301274675', creation_time=1742975277849, experiment_id='148508904301274675', last_update_time=1742975277849, lifecycle_stage='active', name='mlflow-lab', tags={}>
|
mlflow에서 모델을 돌릴때 그래프를 저장할 수 있습니다. 여러가지 모델을 돌리면 parameter마다 그래프가 어떻게 달라지는지 확인해볼 필요가 있기에 Visualization함수를 만듭니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
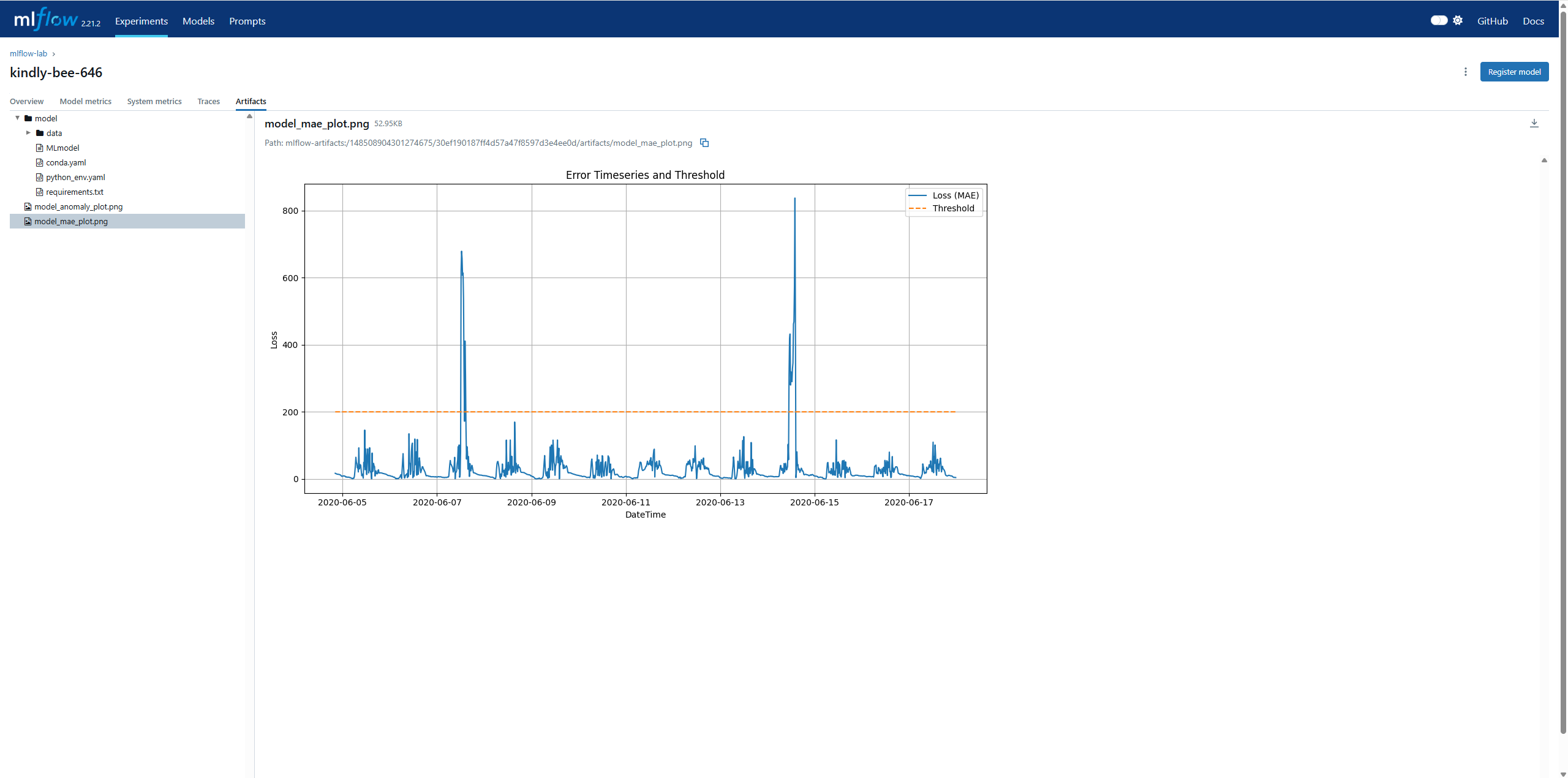
| def mae_visualization(scores):
scores['datetime'] = df_timestamp.loc[1893:].values
scores['real AC'] = test['AC_POWER'].values
scores["loss_mae"] = (scores['real AC'] - scores['AC_POWER']).abs()
scores['Threshold'] = 200
scores['Anomaly'] = np.where(scores["loss_mae"] > scores["Threshold"], 1, 0)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.plot(scores['datetime'], scores['loss_mae'], label='Loss (MAE)')
plt.plot(scores['datetime'], scores['Threshold'], label='Threshold', linestyle='--')
plt.title("Error Timeseries and Threshold")
plt.xlabel("DateTime")
plt.ylabel("Loss")
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("./plot/model_mae_plot.png")
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
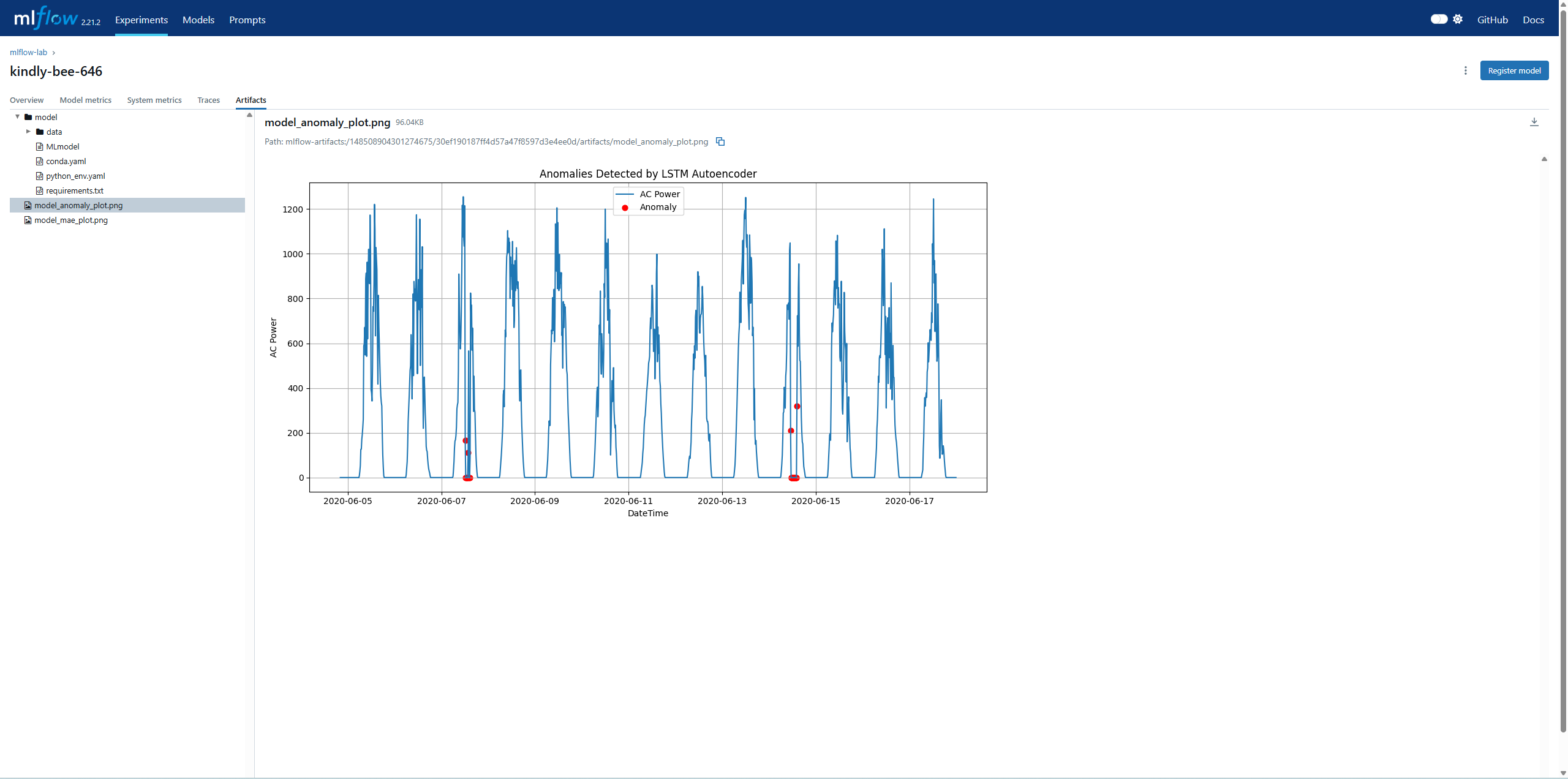
| def anomaly_visualization(scores):
anomalies = scores[scores['Anomaly'] == 1][['real AC']]
anomalies = anomalies.rename(columns={'real AC': 'anomalies'})
scores = scores.merge(anomalies, left_index=True, right_index=True, how='left')
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.plot(scores["datetime"], scores["real AC"], label='AC Power')
plt.scatter(scores["datetime"], scores["anomalies"], color='red', label='Anomaly', s=40)
plt.title("Anomalies Detected by LSTM Autoencoder")
plt.xlabel("DateTime")
plt.ylabel("AC Power")
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("./plot/model_anomaly_plot.png")
|
with mlflow.start_run()을 사용하여 mlflow에 실행시킬 명령어를 작성합니다. 끝에는 mlflow.end_run()을 사용하여 mlflow가 끝났다는 것을 명시합니다.
for문을 통하여 설정한 parameter를 반복하여 최적의 paramter를 찾을 수 있습니다.
또한, log_param을 설정하면 UI에서 각 paramter를 확인하고 비교할 수 있습니다. log_artifact를 설정하면 mlflow ui에서 데이터(이미지, csv등)을 각 모델에서 들어가 볼 수 있습니다.
이외의 다양한 mlflow 설정들은 https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| for batch_size_search in [10,15,20]:
for learning_rate_search in [0.001,0.01,0.1]:
with mlflow.start_run(log_system_metrics=True):
epochs = 10
batch_size = batch_size_search
learning_rate = learning_rate_search
mlflow.log_param("epochs", epochs)
mlflow.log_param("batch_size", batch_size)
mlflow.log_param("learning_rate", learning_rate)
X_tensor = torch.tensor(X_train, dtype=torch.float32)
dataset = TensorDataset(X_tensor, X_tensor)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
# model traning
model = model_traning(epochs, learning_rate, dataloader)
# model evaluation
model.eval()
X_test_tensor = torch.tensor(X_test, dtype=torch.float32)
with torch.no_grad():
X_pred = model(X_test_tensor).numpy()
X_pred = X_pred.reshape(X_pred.shape[0], X_pred.shape[2])
X_pred = scaler.inverse_transform(X_pred)
X_pred = pd.DataFrame(X_pred, columns=train.columns)
X_pred.index = test.index
# visualization
mae_visualization(X_pred)
anomaly_visualization(X_pred)
mlflow.log_metric("anomaly cnt", len(X_pred[X_pred['Anomaly'] == 1]))
mlflow.log_artifact("./plot/model_mae_plot.png")
mlflow.log_artifact("./plot/model_anomaly_plot.png")
mlflow.pytorch.log_model(model, "model")
mlflow.end_run()
|
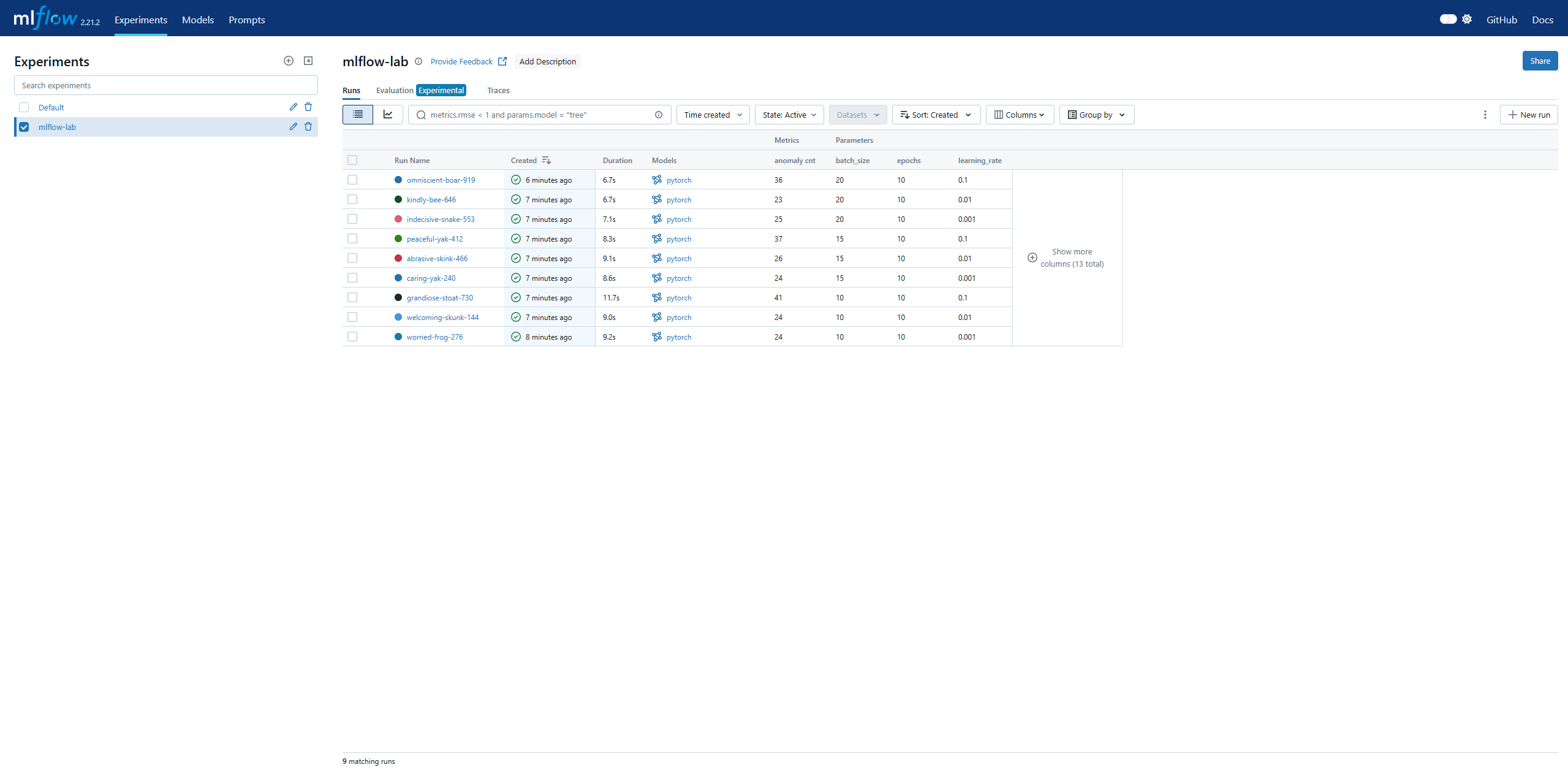
MLflow UI를 확인해보면
설정한 paramter들로 학습된것을 확인할 수 있습니다. log_paramter에 설정한 값은 각 오른쪽을 통해 확인할 수 있습니다. 만약 accuracy, precision, recall, fl score등을 넣고 싶으면 log_matric에 설정하면 확인할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해서 가장 잘 맞춘 모델의 paramter를 확인할 수 있습니다.
Run Name을 클릭하여 상단의 Artifacts를 확인하면 저장한 그래프를 확인할 수 있습니다.
참고자료